(Minimizing
disruption through effective risk management - with services that focus
on health and safety, food safety and information security)
 |
OHSAS 18001(Occupational Health & Safety System)
|
Managing risk to reduce accidents, comply with legislation and improve performance |
OVERVIEW |
The OHSAS 18001 is the international Occupational Health and Safety Management System standard.
The
implementation / certification to OHSAS 18001 ensure that your
operations are safe for your employees and the surrounding environment.
It also proves that you are actively working to ensure health and
safety of employees. Adherence to Legislative / regulatory requirements
and continual improvement are two important aspects of OHSAS 18001.
OHSAS 18001 has been developed to be compatible with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 to allow easy integration. |
Who is it relevant to? |
These standards are applicable to companies of any size, but is especially relevant to the companies :
- with a large work force
- manual or heavy work tasks
- high risk work environments.
The elements of OHSAS 18001 include |
| Policy and commitment |
| Legal requirements |
| Hazard identification, risk assessment & risk controls |
| Objectives & Management Programs |
| Organization & personnel |
| Training, Communication & Consultation |
| Documentation & records |
| Operational Controls |
| Emergency Readiness |
| Measurement & monitoring |
| Accident & incident investigation, corrective & preventive action |
| Audit & Review |
|
|
|
 |
ISO/IEC 27001 (Information Security Management System) |
Protecting information - your most valuable asset |
| |
OVERVIEW |
The ISMS (Information Security
Management System) enables an organization to establish an effective
framework for managing information security. ISO 27001 defines
comprehensive requirements for ISMS that deals with all the technical
and human aspects in information security in all its operational
processes. Companies can be independently audited to ISO 27001and
achieve registration to show their customers, partners and regulatory
bodies that their processes are secure in handling information.
The goal of ISO 27001 is to provide a common base for developing
organizational security standards and effective security management
practices and to provide confidence in inter-organizational dealings. |
Who is it relevant to? |
| ISO/IEC
27001 is suitable for any organization, large or small, in any sector
or part of the world. The standard is particularly suitable where the
protection of information is critical, such as in the finance, health,
public and IT sectors. ISO/IEC 27001 is also highly effective for
organizations who manage information on behalf of others, such as IT
outsourcing companies: it can be used to assure customers that their
information is being protected. |
IQS STEP BY STEP APPROACH TO ISO/IEC 27001 CERTIFICATION |
| The
flow chart gives a high level view of the major steps in the
process. This is a generic diagram - the details will vary from
situation to situation. The main activities are as follows : |
 |
Top management commitment |
 |
Define ISMS scope |
 |
Inventory your information assets |
 |
Conduct an information security risk assessment |
 |
(a) Prepare a Statement of Applicability.
(b) Prepare Risk Treatment Plan. |
 |
Develop ISMS implementation program Run the ISMS implementation program |
 |
Operate the ISMS Collect ISMS operational artifacts |
 |
Review compliance |
 |
Undertake corrective actions |
 |
Conduct a internal audit |
 |
Final Certification audit |
| |
|
|
|
 |
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points)
Managing food safety risks.
|
| |
OVERVIEW |
Hazard
Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) is the main platform for
international legislation and good manufacturing practices for all
sectors of the food industry. HACCP also forms a key component of many
certified compliance standards and is recognized as a main element of
international trade in food products.
HACCP is a risk management tool recognized internationally for use in
the proactive management of food safety issues. A HACCP system helps
you to focus on the hazards that affect food safety through hazard
identification and to establish critical control limits at critical
points during the production process.
The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) has developed international
codex standards and guidelines with the aim of providing a high level
of consumer protection and fair practice in the international trade of
food and agricultural products.
IQS HACCP implementation methodology is intended to meet, as a
minimum, the CAC’s General Principles of Food Hygiene and HACCP, but it
can also be tailored to include other Codex product-related codes of
practice or guidelines as well as any national standard requirements. |
Who is it relevant to? |
HACCP
is relevant to all sectors of the food industry, including primary
producers, manufacturers, processors and food service operators who
want to demonstrate their compliance with national or international
food safety legislation requirements.
|
|
|
 |
ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management System) |
Managing food safety risks across the food supply chain. |
OVERVIEW |
This
International Standard specifies the requirements for a food safety
management system that combines the generally recognized key elements
to ensure food safety along the food chain, up to the point of final
consumption. ISO 22000 will make it easier for organizations world wide
to implement the Codex HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control
Point) system for food hygiene in a harmonized manner, which does not
vary with the country or food product concerned. ISO 22000 has been
aligned with ISO 9001 in order to enhance the compatibility of the food
safty management with overall performance.
The standard has been developed within ISO by experts from the food
industry, along with representatives of Codes Alimentarius
Commission, the body jointly established by the United Nations' Food
and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (WHO)
to develop food standards.
ISO 22000- Requirements for any organization in the food Chain
was published on 1 st Sept 2005. It is first in family of food safety
management systems standards. |
Who is it relevant to? |
ISO
22000 is designed to allow all types or organizations within the food
chain to implement a food safety management system. These range from
feed producers, primary producers, food manufacturers, transport and
storage operators and subcontractors to retail and food service
out-lets - together with related organizations such as producers of
equipment, packaging material, cleaning agents, additives and
ingredients. |
REQUIREMENTS |
| The
ISO 22000 international standard specifies the requirements for a food
safety management system that involves the following elements: |
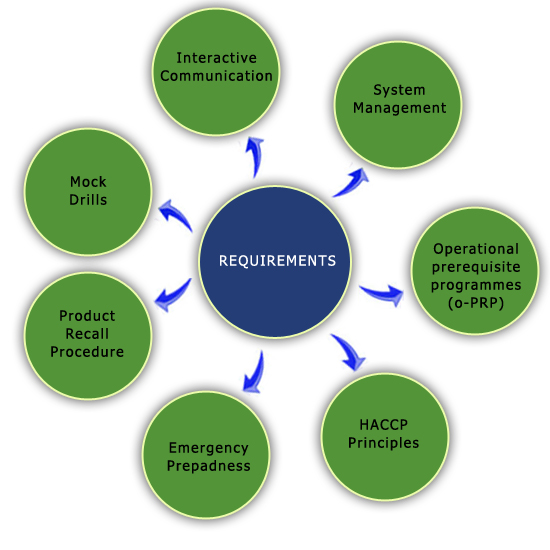 |
| ISO
22000 can be applied independently of other management system standards
or integrated with existing management system requirements. |
|
|
|
 |
BRC Global standard – Food |
Ensuring consumer confidence in food safety. |
| |
OVERVIEW |
Developed
by the British Retail Consortium (BRC), a UK trade organization that
represents the interests of UK retailers, the BRC's Global Standard for
Food Safety was created to establish a standard for due diligence
and supplier approval.
The standard has been adopted by food manufacturers throughout the
world, especially by those organizations supplying British retailers.
Third-party certification to the standard helps manufacturers, brand
owners and retailers fulfil their legal obligations and safeguard
consumers. The standard covers a comprehensive scope of product safety
areas, as well as the legal and due diligence responsiblities of both
the supplier and the retailer. |
Who is it relevant to? |
| It
is particularly suitable for companies supplying food products to
UK retailers, regardless of the product or country of origin. In most
cases certification to this standard is a pre-condition for supplying
to UK retailers. It has been adopted by organizations throughout
the world. |
Requirements |
| The
principal requirements of the standard are the adoption and
implementation of a HACCP system, a documented and effective quality
management system and a control of factory environmental standards,
products, processes and personnel |
|
|
|
 |
ISO/IEC 17025:2005 |
Formal Recognition of Testing and Calibration Laboratories |
OVERVIEW |
ISO/IEC
17025:2005 specifies the general requirements for the competence to
carry out tests and/or calibrations, including sampling. It covers
testing and calibration performed using standard methods, non-standard
methods, and laboratory-developed methods.
Laboratory Accreditation
provides formal recognition of competent laboratories, thus providing a
ready means for customers to find reliable testing and calibration
services .Society also needs to know the technically competent
laboratory in fields such as Medical, Forensic, Food Testing etc
ISO/IEC 17025:2005 is for use by laboratories in developing their
management system for quality, administrative and technical operations.
Compliance with regulatory and safety requirements on the operation of
laboratories is not covered by ISO/IEC 17025:2005.
In common with
other ISO quality standards, ISO/IEC 17025 requires continual
improvement. Regular internal audits are expected to indicate
opportunities to make the test or calibration better than it was.
Additionally, the laboratory will be expected to keep abreast of
scientific and technological advances in relevant areas.
Unlike most ISO standards for systems, third party auditing and
appraisal of the laboratory is not usually carried out by a
certification body, but by the national organisation(NABL in India)
responsible for accreditation. Laboratories are therefore "ACCREDITED" under ISO/IEC 17025, rather than "certificated" (c.f. ISO 9000 series).
The original standard, ISO/IEC 17025:1999 was withdrawn and replaced by
ISO/IEC 17025:2005, though the differences between the two standards
are small. |
Who is it relevant to? |
It
is applicable to all organizations performing tests and/or
calibrations. These include, for example, first-, second- and
third-party laboratories, and laboratories where testing and/or
calibration forms part of inspection and product certification.
ISO/IEC 17025:2005 is applicable to all laboratories regardless of the
number of personnel or the extent of the scope of testing and/or
calibration activities.. |
REQUIREMENTS |
| A
laboratory wishing to be accredited by NABL must have a Quality Manual
on its Quality System satisfying the requirements as described in
various clauses of ISO/IEC 17025 . Quality System documentation and its
implementation by the laboratories shall be verified by the Assessors
for its compliance in accordance with ISO/IEC 17025 . The laboratory
management shall demonstrate to the NABL Assessment Team that all
requirements as laid down in the ISO/IEC 17025, Specific Criteria and
other Guidelines / Requirements of NABL are being followed. |
|
|
|
 |
ISO 15189:2003 |
formal recognition of medical laboratories |
| |
OVERVIEW |
| ISO 15189:2003 specifies requirements for quality and competence particular to medical laboratories. |
Who is it relevant to? |
| The medical laboratories seeking accreditation by NABL are assessed in accordance with ISO 15189:2003 . |
REQUIREMENTS |
| A
laboratory wishing to be accredited by NABL must have a Quality Manual
on its Quality System satisfying the requirements as described in
various clauses of ISO 15189 standard. Quality System
documentation and its implementation by the laboratories shall be
verified by the Assessors for its compliance in accordance with
ISO 15189 standard. The laboratory management shall demonstrate to the
NABL Assessment Team that all requirements as laid down in the ISO
15189 standard, Specific Criteria and other Guidelines / Requirements
of NABL are being followed. |
|
|
|
 |
WHO-GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) |
Ensuring confidence in pharmaceuticals production |
| |
OVERVIEW |
Good
manufacturing practice (GMP) is a system for ensuring that products are
consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.
There must be systems to provide documented proof that correct
procedures are consistently followed at each step in the manufacturing
process - every time a product is made.
WHO has established detailed guidelines for good manufacturing
practice. Many countries have formulated their own requirements for GMP
based on WHO GMP. Others have harmonized their requirements, for
example in the Association of South-East Asian Nations (ASEAN), in the
European Union and through the Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention.
WHO GMP guidelines are available online. |
Who is it relevant to? |
It is designed to minimize the “RISKS” involved in any pharmaceutical, biotech cosmetic or food production.
The main “RISKS” are:
-
unexpected contamination of products, causing damage to health or even death
-
loss of quality of end product or yield of product
-
incorrect labels on containers, which could mean that patients receive the wrong medicine or unintended use
-
insufficient or too much active ingredient, leading to ineffective results or adverse effects
|
|
 |
ISO 13485 Medical Devices |
Ensuring confidence in medical device safety |
| |
OVERVIEW |
| ISO
13485 is an international standard that specifies requirements for a
quality management system that can be used by an organization for the
design and development, production, installation, and servicing of
medical devices. This standard can also be used by international and
external parties, including certification bodies, for assessment of the
organization's ability to meet customer and regulatory requirements.
The quality management system requirements specified in the ISO
13485:2003 standard complements technical requirements for products.
The primary purpose of the ISO 13485:2003 standard is to facilitate
harmonized medical device regulatory requirements for quality systems. |
Who is it relevant to? |
All
requirements of the ISO 13485:2003 standard are specific to
organizations providing medical devices, regardless of the type or
size. |